Canonicalization
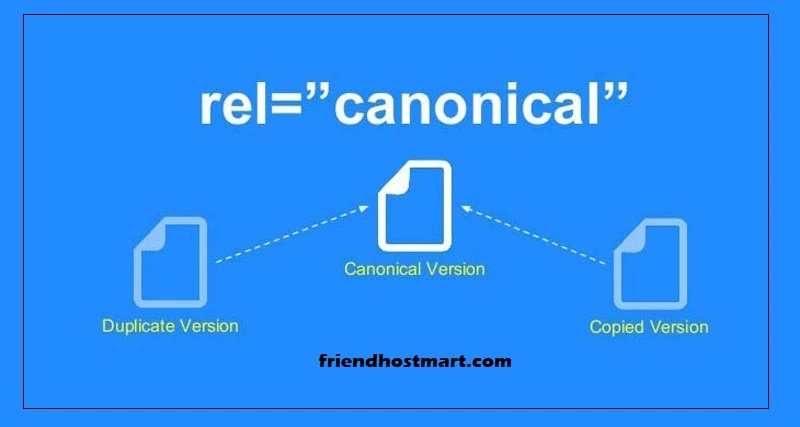
What is a canonical tag?
A canonical tag (aka “rel canonical”) is a way of telling search engines that a specific URL represents the master copy of a page. Using the canonical tag prevents problems caused by identical or “duplicate” content appearing on multiple URLs. Practically speaking, the canonical tag tells search engines which version of a URL you want to appear in search results.
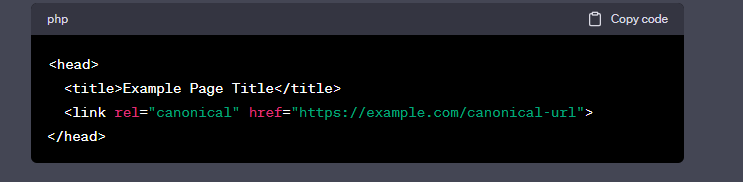
Code sample

Why does canonicalization matter?
Duplicate content is a complicated subject, but when search engines crawl many URLs with identical (or very similar) content, it can cause a number of SEO problems. First, if search crawlers have to wade through too much duplicate content, they may miss some of your unique content. Second, large-scale duplication may dilute your ranking ability. Finally, even if your content does rank, search engines may pick the wrong URL as the “original.” Using canonicalization helps you control your duplicate content.
The problem with URLs
You might be thinking “Why would anyone duplicate a page?” and wrongly assume that canonicalization isn’t something you have to worry about. The problem is that we, as humans, tend to think of a page as a concept, such as your homepage. For search engines, though, every unique URL is a separate page.
For example, search crawlers might be able to reach your homepage in all of the following ways:
- http://www.example.com
- https://www.example.com
- http://example.com
- http://example.com/index.php
- http://example.com/index.php?r…
To a human, all of the URLs that lead to the same page may seem like just one page. However, to a search crawler, each of these URLs is considered a unique “page.” In the example provided, there are five different versions of the homepage, each with its own URL. In reality, the number of variations can be much larger, especially with modern content management systems (CMS) and dynamic, code-driven websites.
CMS platforms and dynamic websites tend to exacerbate the problem of duplicate content even more. These platforms may automatically add tags, create multiple paths to the same content, and add URL parameters for things like searches, sorts, and currency options. As a result, you may end up with thousands of duplicate URLs on your site without even realizing it. This can have a negative impact on your search rankings, which is why it’s important to address canonicalization issues proactively.
Canonical tag best practices
Yes, duplicate content issues can be challenging to navigate, but there are some important considerations to keep in mind when using the canonical tag:
- Use the canonical tag only when necessary: It’s important to use the canonical tag only when you have multiple versions of the same page. If you don’t have any duplicate content issues, then there’s no need to use the canonical tag.
- Specify the canonical URL: When using the canonical tag, it’s essential to specify the canonical URL clearly. This tells search engines which version of the page is the primary one and helps consolidate link equity.
- Make sure the canonical URL is valid and accessible: The canonical URL you specify must be a valid and accessible URL that search engines can crawl. Otherwise, the canonical tag won’t be effective in resolving duplicate content issues.
- Avoid using the canonical tag for pages with different content: The canonical tag should only be used for pages that have identical or very similar content. If the content on two pages is substantially different, then using the canonical tag isn’t appropriate.
- Keep an eye on your website’s performance: Even with the use of the canonical tag, duplicate content issues can still occur. It’s essential to monitor your website’s performance and make adjustments as needed to maintain search rankings and traffic.
How to audit your canonical tags for SEO
Yes, those are all important things to check when auditing your canonical tags for optimal SEO performance. Here’s a more detailed checklist:
- Check if the page has a canonical tag: Make sure that each page on your website has a canonical tag if necessary. Remember, you should only use the canonical tag if you have duplicate content issues.
- Verify if the canonical tag points to the right page: Ensure that the canonical tag points to the correct page on your website. If the canonical tag points to an incorrect or non-existent page, it can negatively impact your search rankings.
- Check if all pages are crawlable and indexable: Ensure that all pages on your website are crawlable and indexable by search engines. If a page is not crawlable or indexable, it won’t be included in search results, even if it has a canonical tag.
- Check for self-referencing canonical tags: Make sure that pages don’t have self-referencing canonical tags. If a page references itself as the canonical page, it can cause indexing issues and negatively impact your search rankings.
- Check for consistency across canonical tags: Ensure that canonical tags are consistent across pages with similar content. If canonical tags are inconsistent, it can create confusion for search engines and negatively impact your search rankings.
- Check for implementation errors: Check for implementation errors such as missing or incorrectly formatted canonical tags. These errors can cause indexing issues and negatively impact your search rankings.
Yes, pointing the canonical tag at a URL that is blocked by robots.txt or set to “noindex” can be a common mistake, as it can cause confusion for search engines and impact your SEO performance negatively. Here are a few common ways to inspect and audit your canonical tags:
- Use a website crawler: Use a website crawler tool, such as Screaming Frog or Sitebulb, to crawl your website and identify any pages that have incorrect or missing canonical tags. This can help you identify and fix issues quickly.
- Check the source code: Inspect the source code of your website’s pages to ensure that the canonical tags are correctly implemented and pointing to the correct URL. You can do this manually or by using browser extensions, such as Chrome’s “View Page Source” or “Inspect Element” features.
- Use Google Search Console: Google Search Console is a free tool that provides insights into your website’s performance in Google search results. You can use it to check for duplicate content issues and to see if Google has detected any canonicalization errors on your website.
- Check your XML sitemap: Check your XML sitemap to ensure that all URLs on your website have been included and are correctly indexed. This can help you identify any issues with canonical tags or other indexing issues.
By regularly auditing and monitoring your website’s canonical tags, you can help ensure that your website is correctly optimized for search engines, which can lead to improved search rankings and increased traffic.